|
Größe: 12097
Kommentar:
|
Größe: 12138
Kommentar:
|
| Gelöschter Text ist auf diese Art markiert. | Hinzugefügter Text ist auf diese Art markiert. |
| Zeile 165: | Zeile 165: |
| {{attachment:ggp6.png}} | [[attachment:ggp6.png|{{attachment:ggp6.png||width=300}}]] |
| Zeile 233: | Zeile 234: |
| Create the five plots and save them into a file. * create a plot using ggplot, map the variable EC1 to x and use geom\_bar() * now to the plot again, but add another aesthetic: fill (colour of the filling); map fill to Stim.Type * add the position argument to geom\_bar(), set it to "fill" * now add \texttt{facet\_wrap(~testid)} to show the same graph per time * make a graph facetted per child showing stacked hit/incorrect bars with time on the x axis | Create the five plots and save them into a file. * create a plot using ggplot, map the variable EC1 to x and use geom_bar() * now to the plot again, but add another aesthetic: fill (colour of the filling); map fill to Stim.Type * add the position argument to geom_bar(), set it to "fill" * now add facet_wrap(~testid) to show the same graph per time * make a graph facetted per child showing stacked hit/incorrect bars with time on the x axis |
The ggplot2 Package
- ggplot2 is - like lattice based on the grid graphics system (Paul Murrell)
- graphics and parts of graphics are objects and they are manipulable
Structure of a ggplot Object
begin with an empty object to see the structure:
- what we see are empty place holders
- when we use str() to explore the structure of the object we see that it is a list with length 9
1 > str(po)
2 List of 9
3 List of 9
4 $ data : list()
5 ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "waiver"
6 $ layers : list()
7 $ scales :Reference class 'Scales' [package "ggplot2"] with 1 fields
8 ..$ scales: NULL
9 ..and 21 methods, of which 9 are possibly relevant:
10 .. add, clone, find, get_scales, has_scale, initialize, input, n,
11 .. non_position_scales
12 $ mapping : list()
13 $ theme : list()
14 $ coordinates:List of 1
15 ..$ limits:List of 2
16 .. ..$ x: NULL
17 .. ..$ y: NULL
18 ..- attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "cartesian" "coord"
19 $ facet :List of 1
20 ..$ shrink: logi TRUE
21 ..- attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "null" "facet"
22 $ plot_env :<environment: R_GlobalEnv>
23 $ labels : list()
24 - attr(*, "class")= chr [1:2] "gg" "ggplot"
Structure of a ggplot Object
Now we fill this structure - first the three main steps:
- the first argument to ggplot is data
- then specify what graphics shapes you are going to use to view the data (e.g. geom_line() or geom_point()).
- specify what features (or aesthetics) will be used (e.g. what variables will determine x- and y-locations) with the aes() function
- if these aesthetics are intented to be used in all layers it is more convenient to specify them in the ggplot object
Feed the Object
- first we create a little sample data frame\small
1 > x1 <- 1:10; y1 <- 1:10; z1 <- 10:1
2 > l1 <- LETTERS[1:10]
3 > a <- 10; b <- (0:-9)/10:1
4 > ex <- data.frame(x=x1,y=y1,z=z1,l=l1,a=a,b=b)
5 > ex
6 x y z l a b
7 1 1 1 10 A 10 0.0000000
8 2 2 2 9 B 10 -0.1111111
9 3 3 3 8 C 10 -0.2500000
10 4 4 4 7 D 10 -0.4285714
11 5 5 5 6 E 10 -0.6666667
12 6 6 6 5 F 10 -1.0000000
13 7 7 7 4 G 10 -1.5000000
14 8 8 8 3 H 10 -2.3333333
15 9 9 9 2 I 10 -4.0000000
16 10 10 10 1 J 10 -9.0000000
- then we create a ggplot object containing the data and some standard aesthetics (here we define the x and the y positions)
- add one or more geoms, we begin with geom_point
Layers
- ggplot() creates an object - every "+" adds something to this object (change the object)
- the default method of ggplot() is print(), which creates the plot
- it is better to store the object - so you can change it (e.g. you can change the data frame)
Layers
- so we add another layer, which adds a label to the points (use geom\_text)
- aes(label=l) maps the l variable to the label aesthetic, and hjust and vjust define where our labels are placed
Layers
imagine you have worked a little time on a plot - and then you detect a mistake in your data, so the real data frame looks different
- so you can replace the old, wrong data by the new data (using %+%)
Layers
1 > p2 %+% ex2
Layers
- by using the line geom you can join the points (we use the new data)
Layers
- you can also join the points in the order of the data fram by using the path geom instead\footnotesize
Layers
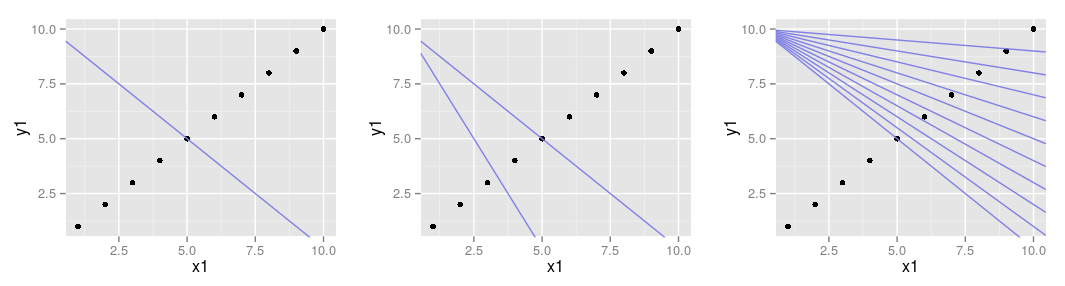
Adding extra lines:
- there are three geoms: abline, vline, hline
- abline adds one or more lines with specified slope and intercept to the plot\footnotesize
Layers
- adding lines referring to the data frame
Layers
- the same works for the hline and the vline geom which add horizonal and vertical line(s)
- argument: yintercept, xintercept respectively
- setting and mapping are possible
Other Common Layers
- some other layers for 1 continuous variable:
- geom_boxplot()
- geom_histogram()
- geom_density()
- some other layers for 1 discrete variable:
- geom_bar()
- some other layers for 2 or more continuous variables:
- geom_smooth()
- geom_density2d()
- geom_contour()
- geom_quantile()
Exercises
- use our data frame or load it: load("20150310data.rdata")
- create a new variable EC1 containing the first 2 letters of the Event.Code column, use the function str_sub() from the stringr package (type ?str_sub to get help)
Exercises
1 > data$EC1 <- factor(str_sub(data$Event.Code,1,2))
2 > head(data)
3 Subject Sex Age_PRETEST Trial Event.Type Code Time TTime Uncertainty
4 1 1 f 3.11 7 Response 2 103745 2575 1
5 2 1 f 3.11 12 Response 2 156493 2737 1
6 3 1 f 3.11 17 Response 2 214772 6630 1
7 4 1 f 3.11 22 Response 1 262086 5957 1
8 5 1 f 3.11 27 Response 2 302589 272 1
9 6 1 f 3.11 32 Response 1 352703 7197 1
10 Duration Uncertainty.1 ReqTime ReqDur Stim.Type Pair.Index Type Event.Code
11 1 2599 3 0 next hit 7 Picture RO26.jpg
12 2 2800 2 0 next incorrect 12 Picture RO19.jpg
13 3 6798 2 0 next hit 17 Picture RS23.jpg
14 4 5999 2 0 next incorrect 22 Picture OF22.jpg
15 5 400 2 0 next hit 27 Picture AT08.jpg
16 6 7398 2 0 next hit 32 Picture AT30.jpg
17 testid EC1
18 1 test2 RO
19 2 test2 RO
20 3 test2 RS
21 4 test2 OF
22 5 test2 AT
23 6 test2 AT
Exercises
Create the five plots and save them into a file.
- create a plot using ggplot, map the variable EC1 to x and use geom_bar()
- now to the plot again, but add another aesthetic: fill (colour of the filling); map fill to Stim.Type
- add the position argument to geom_bar(), set it to "fill"
- now add facet_wrap(~testid) to show the same graph per time
- make a graph facetted per child showing stacked hit/incorrect bars with time on the x axis
Exercises
- create a plot using ggplot, map the variable EC1 to x and use geom\_bar()
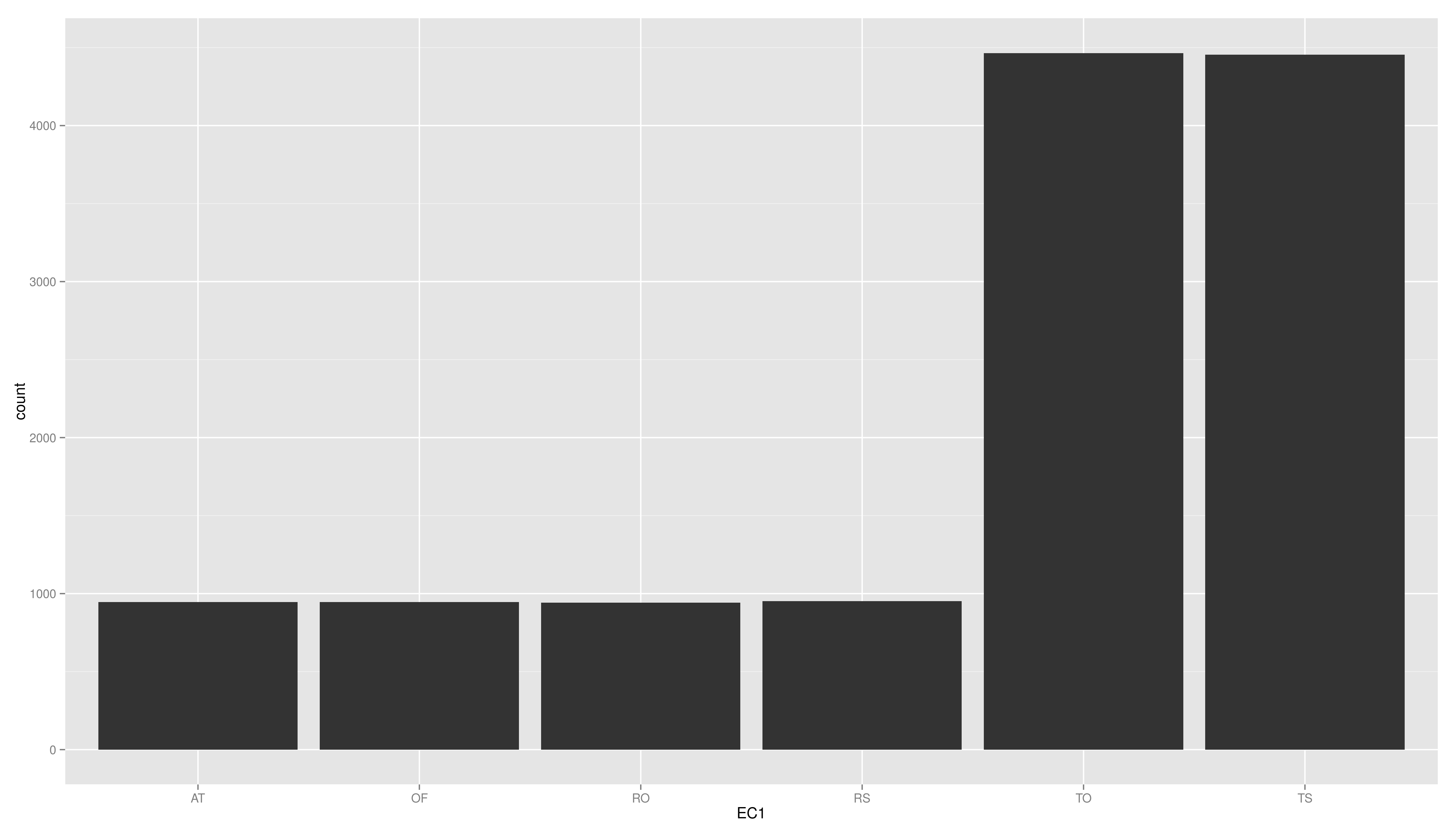
Exercises
- now to the plot again, but add another aesthetic: fill (colour of the filling); map fill to Stim.Type
<img alt='sesssion2/plot2.png' src='-1' />
Exercises
- add the position argument to geom\_bar(), set it to "fill"
<img alt='sesssion2/plot3.png' src='-1' />
Exercises
- now add \texttt{facet\_wrap(~testid)} to show the same graph per time
<img alt='sesssion2/plot4.png' src='-1' />
Exercises
- now add \texttt{facet\_wrap(~testid)} to show the same graph per time
<img alt='sesssion2/plot4a.png' src='-1' />
Exercises
- make a graph facetted per child showing stacked hit/incorrect bars with time on the x axis
<img alt='sesssion2/plot5.png' src='-1' />
Introduction
The dplyr package makes each of these steps as fast and easy as possible by:
- Elucidating the most common data manipulation operations, so that your options are helpfully constrained when thinking about how to tackle a problem.
- Providing simple functions that correspond to the most common data manipulation verbs, so that you can easily translate your thoughts into code.
- Using efficient data storage backends, so that you spend as little time waiting for the computer as possible.
Scales
What if we want to change the colours?
- this leads to another important type of component not yet mentioned
- if you map a variable to a aesthetic is these done in a default way, in this case some reddish colour is mapped to hit while light blue is mapped to incorrect; in addition a discrete range of colours is automatically used
- these rules of mapping are called scales
- different type of scales exists for the axes, colours, shapes etc, some of them exists in discrete and continuous versions, some in just one of them (in general one can say, everytime there can be a legend there is a scale)
- the name convention: scale\_aesthetic\_specification. for example scale\_x\_discrete for customizing a discrete x axis (e.g. in barplots)
Changing a Scale
- to change our discrete colour scale for the filling we type \footnotesize
<img alt='sesssion2/ggp10.png' src='-1' />
Changing a Scale
There are other ways to customize a discrete colour/fill scales
- scale\_colour\_grey()
- scale\_colour\_hue()
- scale\_colour\_brewer()
Changing a Scale
1 > ggplot(data,aes(x=EC1,fill=Stim.Type)) +
2 + geom_bar(position = "fill") +
3 + facet_wrap(~testid,scales = "free") +
4 + scale_fill_grey()
5 > ggplot(data,aes(x=EC1,fill=Stim.Type)) +
6 + geom_bar(position = "fill") +
7 + facet_wrap(~testid,scales = "free") +
8 + scale_fill_hue(h=c(180,360))
9 > ggplot(data,aes(x=EC1,fill=Stim.Type)) +
10 + geom_bar(position = "fill") +
11 + facet_wrap(~testid,scales = "free") +
12 + scale_fill_brewer(type = "div",palette = 2)